Osteoarthritis Treatment In Elmhurst IL
Feeling joint pain, stiffness, and disability can be demotivating and can significantly affect our daily activities.
One condition that commonly causes these symptoms is osteoarthritis. We will discuss osteoarthritis, who is at
risk, and its causes and symptoms. We will also tackle the various treatment and self-care options available to
alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with this disease.
What Is
Osteoarthritis?

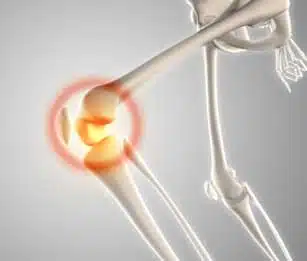
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints, protecting them from damage, breaks down. As a result, bones start rubbing against each other, leading to various symptoms, including pain, stiffness, and disability. This disease can affect any joint, but it most commonly affects.
Who Gets Osteoarthritis?
While Osteoarthritis can happen to anyone, it is more common as one ages or after menopause in
women. Other risk factors include
Joint Injury
Abnormal joint
structure

Genetic defects in joint Cartilage
People with obesity are also at higher risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Causes & Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms
Of Osteoarthritis?

Are you experiencing pain or stiffness in your joints? It could be
possible that you are experiencing the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
This degenerative joint disease can begin slowly and is often localized
in one or a few joints. Pain when using the joint is a common symptom,
which can improve with rest. Some people may experience worse pain
at night during the later stages of the disease. Joint stiffness usually
lasts for less than 30 minutes and can occur in the mornings or after
resting for an extended time. Other symptoms include limited joint
movement, swelling, and a loose feeling or instability. Know that
osteoarthritis symptoms can affect joints differently, so it’s essential
to consult a healthcare professional if you think you may have it.
What Are The Causes Of Osteoarthritis?

Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage and other tissues within the joint break down or change their structure. Other factors that make it more likely for you to get this disease include:
- Aging is a significant risk factor for osteoarthritis.
- Being overweight or obese can also increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- A history of injury or surgery to a joint can increase the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis.
- Overuse of repetitive joint movements may also contribute to the development of Osteoarthritis.
- Joints that do not form correctly or have abnormal structures may increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- A family history of osteoarthritis may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Diagnosis & Treatment
How Do I Know If I Have Osteoarthritis?

There is no single test for osteoarthritis. The diagnosis of
osteoarthritis may include the following steps:
- Provide a medical history that includes your symptoms, any
other medical problems you and your close family members
have, and any medications you take. - Have a physical exam to check your general health, reflexes,
and problem joints. - Having images taken of your joint using X-rays or an MRI to
show loss of joint space, bone damage, bone remodeling,
and bone spurs. - Having blood tests to rule out other causes for symptoms.
- Taking joint fluid samples to look for other causes of joint
pain such as infection or gout.
If you are experiencing joint pain, stiffness, and limited
mobility, consult your doctor for a proper evaluation and
diagnosis of osteoarthritis.
How Is Osteoarthritis Treated?

Treatments for osteoarthritis focus on relieving symptoms and
slowing down the progression of the disease. These include
increasing physical activity, physical therapy, muscle-
strengthening exercises, weight loss, and medications,
including over-the-counter pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), prescription pain relievers, and
corticosteroids. Surgery like joint replacement surgery may be
necessary in severe cases.
Self-care
How Can I Slow Down Osteoarthritis Naturally?
You can slow down osteoarthritis naturally by incorporating the following self-care strategies into
your lifestyle:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra pressure on the joints, leading to increased pain and damage. Weight
loss can reduce the stress on joints and slow the progression of osteoarthritis. - Control blood sugar: High blood sugar levels can affect cartilage structure and increase the risk of developing
osteoarthritis. By controlling blood sugar through a healthy diet and exercise, you can slow the
progression of the disease. - Maintain range of motion: Lack of movement and flexibility can cause muscles, ligaments, and tendons to weaken, leading to increased pain and stiffness. Regular exercise and stretching can improve joint flexibility and
reduce osteoarthritis symptoms. - Protect joints: Avoiding repetitive motions, using proper technique in physical activities, and protecting your joints from injuries can reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Relax: Psychological stress has been linked to the development and progression of osteoarthritis. Relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can reduce stress and improve overall joint health.
By adopting these self-care strategies, you can manage your osteoarthritis symptoms, reduce the need for medication, and slow down the progression of the disease.
Why Choose Orthopedic Specialists
At Orthopedic Specialists, we understand that Osteoarthritis, commonly referred to as degenerative joint disease, can be incredibly painful and limit your mobility, making it challenging to carry out day-to-day activities. That's why our team of dedicated specialists is committed to providing our patients with the best possible care and support throughout their treatment journey. Our approach is centered around early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. We utilize advanced diagnostic techniques and imaging to accurately identify the extent of the disease and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Book Your AppointmentFAQs
Here are some potential risks related to osteoarthritis:
- Pain: Osteoarthritis can cause chronic pain in the affected joints, affecting daily functioning and leading to depression and anxiety.
- Stiffness: In addition to pain, osteoarthritis can cause stiffness in the affected joints, limiting mobility and worsening the condition.
- Reduced range of motion: Over time, osteoarthritis can cause the joints to become less flexible, leading to decreased range of motion and difficulty performing daily activities.
- Disability: In severe cases of osteoarthritis, the condition can lead to disability, limiting the affected person’s ability to work, perform daily activities, or enjoy leisure time.
- Increased risk of falls: Osteoarthritis can increase the risk of falls, leading to fractures, hospitalizations, and other complications.
- Depression and anxiety: Chronic pain and limitations in mobility can lead to depression and anxiety, affecting the overall quality of life for a person with osteoarthritis.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent or manage osteoarthritis-related risks.
Arthritis is a general term used to describe inflammation in the joints, which various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and crystal deposits, can cause. On the other hand, osteoarthritis is a specific type of arthritis caused by the wear and tear of the joints over time.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, typically in older people. It occurs when the cartilage between the joints begins to break down, causing the bones to rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility.
If you have osteoarthritis, you may want to avoid the following:
- High-impact exercises: Activities that put pressure on the joints, such as running, tennis, or jumping, can worsen symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Repetitive movements: Repetitive motions involving the joints, such as typing, can also worsen symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Being sedentary can lead to muscle weakness, stiffness, and joint pain. Maintaining an active lifestyle helps keep the muscles and bones strong and lowers the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Excess weight: Being overweight or obese stresses the joints, leading to increased pain and cartilage damage.
- Alcohol and tobacco: Consuming alcohol and smoking can increase inflammation in the body, which can worsen symptoms of osteoarthritis.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for advice on managing osteoarthritis and identifying specific trigger factors. They can recommend exercises, medications, and other lifestyle changes that can help alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms.
Walking can help reduce osteoarthritis symptoms by improving joint flexibility and strengthening muscles around the joints to support them better. It also helps reduce excess weight, reducing the strain on joints. However, walking on hard surfaces or for prolonged periods may worsen symptoms in some people. It’s important to seek medical advice to develop a walking program that is safe and tailored to individual needs and symptoms.
Currently, there is no cure for osteoarthritis. However, there are several treatments and self-care strategies that can help slow down the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms. For instance, regular exercise, weight loss, and medication can help reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, some studies suggest that stem cell and platelet-rich plasma therapy may help regenerate cartilage and reduce symptoms in some people. However, further research is needed to determine the effectiveness and safety of these treatments in reversing osteoarthritis.
Here are some exercises that are commonly recommended for people with osteoarthritis:
- Low-impact aerobic exercises: Walking, cycling, swimming, and water aerobics can help improve cardiovascular health and strengthen the muscles around the affected joints without causing additional stress.
- Range-of-motion exercises: Slow, gentle stretches that move the joints through their full range of motion can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, reducing pain and improving joint support. Examples include leg presses, squats, and resistance band exercises.
- Balance exercises: These exercises can help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls, which can be particularly beneficial for people with osteoarthritis in the hips, knees, or ankles. Examples include standing on one foot, using a balance board or pillow, and practicing Tai Chi.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine to ensure it is safe and tailored to individual needs and abilities.
Osteoarthritis can cause fatigue in some individuals. Chronic pain and discomfort can disrupt sleep, leading to daytime fatigue and exhaustion. Additionally, osteoarthritis can cause stress and anxiety, contributing to fatigue. Pain management strategies, lifestyle changes, and exercises tailored to individual needs and abilities can improve osteoarthritis symptoms and reduce fatigue. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for osteoarthritis management.