Facture Care By Top Orthopedic Surgeon In Elmhurst IL
Orthopedic Specialists is committed to providing exceptional fracture care (trauma) services to patients of all
ages. We understand the impact that fractures can have on your daily life, and we are dedicated to helping you
regain mobility, functionality, and overall quality of life. Our highly skilled orthopedic surgeons and specialists are
experienced in diagnosing and treating various orthopedic trauma and fracture conditions.
Orthopedic Trauma & Fracture Care Conditions
Our expert team specializes in treating fractures and trauma in various areas of the body, including:
Spine

Spine fractures refer to injuries involving the bones of the vertebral column. Spinal fractures can vary in severity, ranging from minor compression fractures to more severe fractures that can lead to spinal cord injury. Treatment options include rest, pain management, bracing, and surgical intervention.
Foot & Ankle
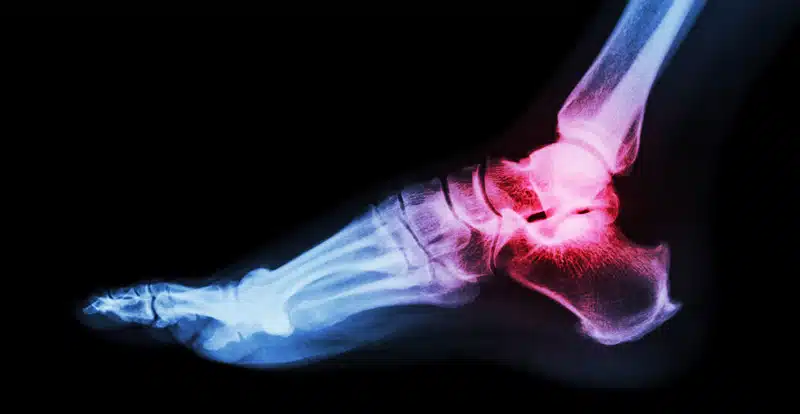
Fractures in the foot and ankle commonly occur due to sports injuries, falls, or accidents. These fractures can involve the bones of the foot, ankle joint, or both. Foot and ankle fractures can cause significant pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Treatment may involve immobilization using casts, splints, or walking boots. Severe fractures may require surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bones.

Hips

Hip fractures primarily affect older adults, often resulting from falls or weakened bones due to osteoporosis. These fractures can cause severe pain, difficulty walking, and loss of independence. Hip fractures typically require surgical treatment, which may involve metal implants or joint replacement to stabilize the fracture and restore function.
Knee
Knee fractures can occur due to high-energy impacts, such as car accidents or sports injuries. These fractures can involve the patella (kneecap), the distal femur (thighbone), or the proximal tibia (shinbone). Treatment options depend on the specific location and severity of the fracture, ranging from non-surgical methods like bracing and immobilization to surgical interventions such as internal fixation or joint replacement.

Shoulders

Fractures of the shoulder can occur due to direct trauma, falls, or sports injuries. They can involve the collarbone (clavicle), the upper arm bone (humerus), or the shoulder blade (scapula). Shoulder fractures can cause pain, limited range of motion, and difficulty performing daily activities. Treatment options include immobilization, physical therapy, or surgical procedures like fracture fixation or joint replacement.
Hand & Upper Extremities

Fractures in the hand, wrist, forearm, and other upper extremities can result from various causes, including falls, direct trauma, or repetitive motion injuries. These fractures can affect the bones, joints, or surrounding structures. Treatment options depend on the specific location and type of fracture and may involve casting, splinting, external fixation, or surgery to restore proper alignment and function.

Treatment Options
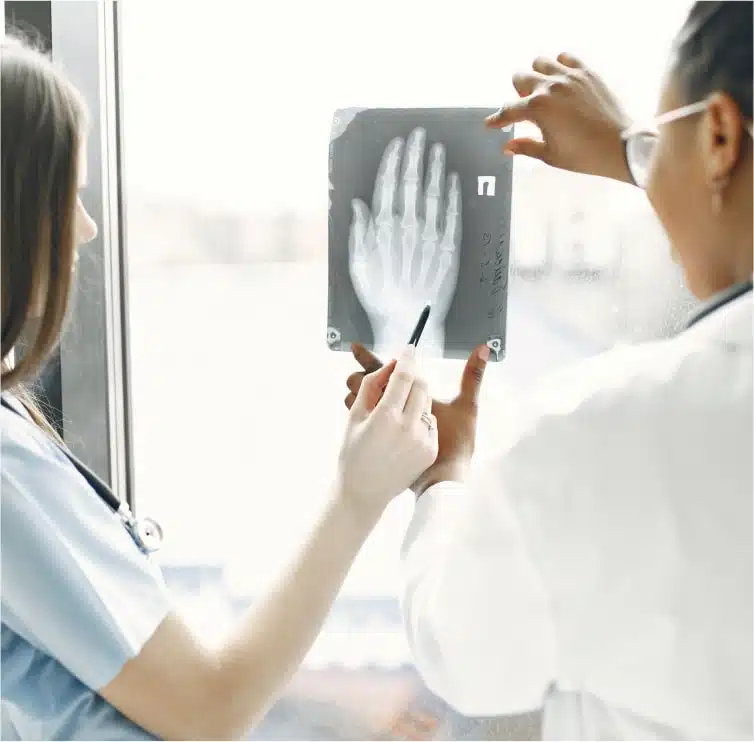

Our fracture care (trauma) approach encompasses surgical and non-surgical treatment options. Based on a comprehensive evaluation of your condition, our experts will recommend the most appropriate course of action:
- Surgical: Our skilled surgeons perform advanced fracture repair procedures using state-of-the-art techniques when necessary. We employ minimally invasive approaches whenever possible, promoting faster recovery and minimizing scarring.
- Non-Surgical: In cases where surgery is not required, we provide non-surgical fracture care options such as casting, immobilization, physical therapy, and pain management techniques. We aim to optimize healing and promote a speedy recovery while minimizing discomfort.
Welcome to Orthopedic
Specialists
When it comes to fracture care (trauma), we will personalize your treatment plan that will result in best outcomes. We won’t let fractures and orthopedic trauma limit your life.
Expertise and
Experience
Our team comprises highly skilled orthopedic surgeons and specialists with extensive experience managing fractures and orthopedic trauma.
Personalized
Care
We understand that each patient is unique, and we provide individualized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs and goals.

Advanced Techniques
and Technology
We stay current with the latest advancements in orthopedic care, utilizing state-of-the-art techniques and technologies to deliver the best possible outcomes.

Comprehensive
Approach
Our approach to fracture care involves a comprehensive evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and customized treatment plan to ensure the best possible recovery.

Patient-Centered
Philosophy
We value open communication and transparency, we provide patient education, we believe in compassionate care ensuring that you are actively involved in your treatment process and recovery.
Please contact us today to schedule a consultation with our team. We are dedicated to helping you recover quickly and regain your best mobility, allowing you to live your life to the fullest
FAQs
Taking care of a fracture involves immobilizing the affected area to allow the bones to heal properly. Here are some steps that can help:
- Seek medical attention immediately. A doctor will examine the injury and take X-rays to determine the severity of the fracture.
- Immobilize the affected area with a splint or cast. This will help to keep the bone in place and reduce pain.
- Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every few hours to help reduce pain and swelling.
- Take over-the-counter pain medication as directed by your doctor.
- Follow your doctor’s advice on when to start using the affected limb again.
Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor the healing progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
While fractures take time to heal, there are a few things you can do to potentially speed up the process:
- Follow your doctor’s orders: It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment and care, including immobilizing the affected area or wearing a cast as directed.
- Eat a healthy diet: Foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein can help promote bone healing. This includes dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and lean meats.
- Get regular exercise: Depending on the severity of your fracture, your doctor may recommend specific exercises or physical therapy to help improve blood flow and promote healing.
- Quit smoking: Smoking has been shown to slow the healing process, so quitting smoking can help you heal faster.
- Consider supplements: Some studies suggest that supplements like calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium may help with bone healing, but it’s important to talk to your doctor before taking any supplements.
Not all fractures can heal quickly; following your doctor’s advice and giving your body time to heal properly is important.
Several factors can slow down fracture healing. Here are a few:
-
- Smoking: Smoking has been shown to reduce the flow and oxygen supply to the bones, leading to slower healing times.
- Poor nutrition: A diet lacking key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein can slow down bone healing.
- Medical conditions like osteoporosis, diabetes, and cancer can slow bone healing.
- Medications: Certain medications, like corticosteroids, can slow down bone healing.
- Infection: Infections can delay or interrupt the healing process.
- Movement or weight-bearing: Depending on the severity and location of the fracture, moving or putting weight on the affected area before it’s fully healed can slow down the healing process and even cause further damage.
Following your doctor’s advice and properly caring for your fracture is important to ensure optimal healing.
The time it takes for a fracture to heal can vary depending on several factors, including the location and severity of the fracture, the age and overall health of the individual, and whether or not the individual follows their doctor’s instructions for treatment and care. Generally, most fractures take 6-12 weeks to heal fully. However, some fractures can take longer to heal, especially in older individuals or those with other health conditions that may affect bone healing.
It’s important to note that even after a fracture has healed, the affected area may take some time for the affected area to regain full strength and mobility. Physical therapy may be necessary to help the individual regain their normal function and range of motion.
The length and severity of pain after a fracture can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the fracture, the location of the fracture, and the individual’s overall health. Acute pain typically lasts a few weeks to a few months after the fracture. As the bone begins to heal, the pain should gradually decrease. However, some individuals may experience chronic pain long after the fracture has healed.
The most complicated fractures to heal occur in areas with limited blood supply, such as the ankle, wrist, and hip. These are nonunion fractures, where the bone fails to heal properly. Other factors can make a fracture difficult to heal.